What is a Chatbot? And How Has AI Changed Them?
Learn how chatbots work, what they cost, and why businesses need them in 2025.
 January 19, 2025
January 19, 2025 9 minute reading
9 minute reading
Online interest in chatbots spiked in 2022 after OpenAI released ChatGPT. Since then, chatbot technology has advanced immensely. Businesses can now use chatbots powered by AI technology to improve customer interactions and handle complex customer queries.
But what exactly makes tools like ChatGPT different from traditional chatbots that rely on predefined scripts? And how do modern chatbots work in practice?
In this article, we’ll break down the distinctions, answer common questions about today’s advanced chatbots, and show you how to get one created easily and affordably.
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a computer program that simulates human conversation through text or voice interactions. Basic chatbots follow predefined rules to provide scripted responses. Modern chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and artificial intelligence to understand context, learn from interactions, and provide personalized responses. Chatbots can automate customer service and improve customer engagement with your brand.
The history and purpose of chatbots
An MIT professor called Joseph Weizenbaum created the world’s first chatbot in 1966, called ELIZA. His purpose was to examine human conversational interaction with computers. Despite ELIZA’s simplicity, many people felt an emotional connection with the “chatterbot,” which shocked Weizenbaum. Despite his efforts to inform users that ELIZA was simply operating off predetermined code instructions, they continued to feel a sense of connection with it.
The term “Eliza effect” comes from this incident. The “Eliza Effect” is when humans attribute and project human characteristics to machines. For example, ChatGPT’s human-sounding answers cause some people to attribute intelligence to it. However, at its most basic level, ChatGPT is a massive autocomplete machine that can predict the next contextually correct word in a sentence. That’s why it can’t compute math or exhibit real human intelligence.
Still, the examples of people’s perceptions of ELIZA and ChatGPT provide insight into why they use chatbots. Humans want human interaction, and chatbots provide the semblance of that interaction. When you implement a sophisticated chatbot on your website that sounds human, you can resolve many customer issues without human intervention.
Chatbots can answer questions, automate repetitive tasks, and streamline workflows, all without involving human agents.
Types of chatbots
A huge number of chatbots exist, such as rule-based chatbots, booking chatbots, menu-based chatbots, AI chatbots, and conversational chatbots. Many of the chatbot categories overlap. For example, you can have a conversational chatbot that’s also a booking chatbot.
Each type of chatbot uses different algorithms to implement its functionality. Let’s look at the major categories of chatbots.
Rule-based chatbots
These chatbots operate using basic keyword detection or menu-based interactions. They’re relatively simple to set up, and plenty of DIY tools can help you build one. However, you’ll need to explicitly define the paths your chatbot will follow based on user responses. While rule-based chatbots may seem straightforward at first, they can quickly become complicated as you add more paths and options.
The purpose of a rules-based chatbot is to handle the simplest customer support queries and then route customers to a human agent if the bot can’t handle the query.
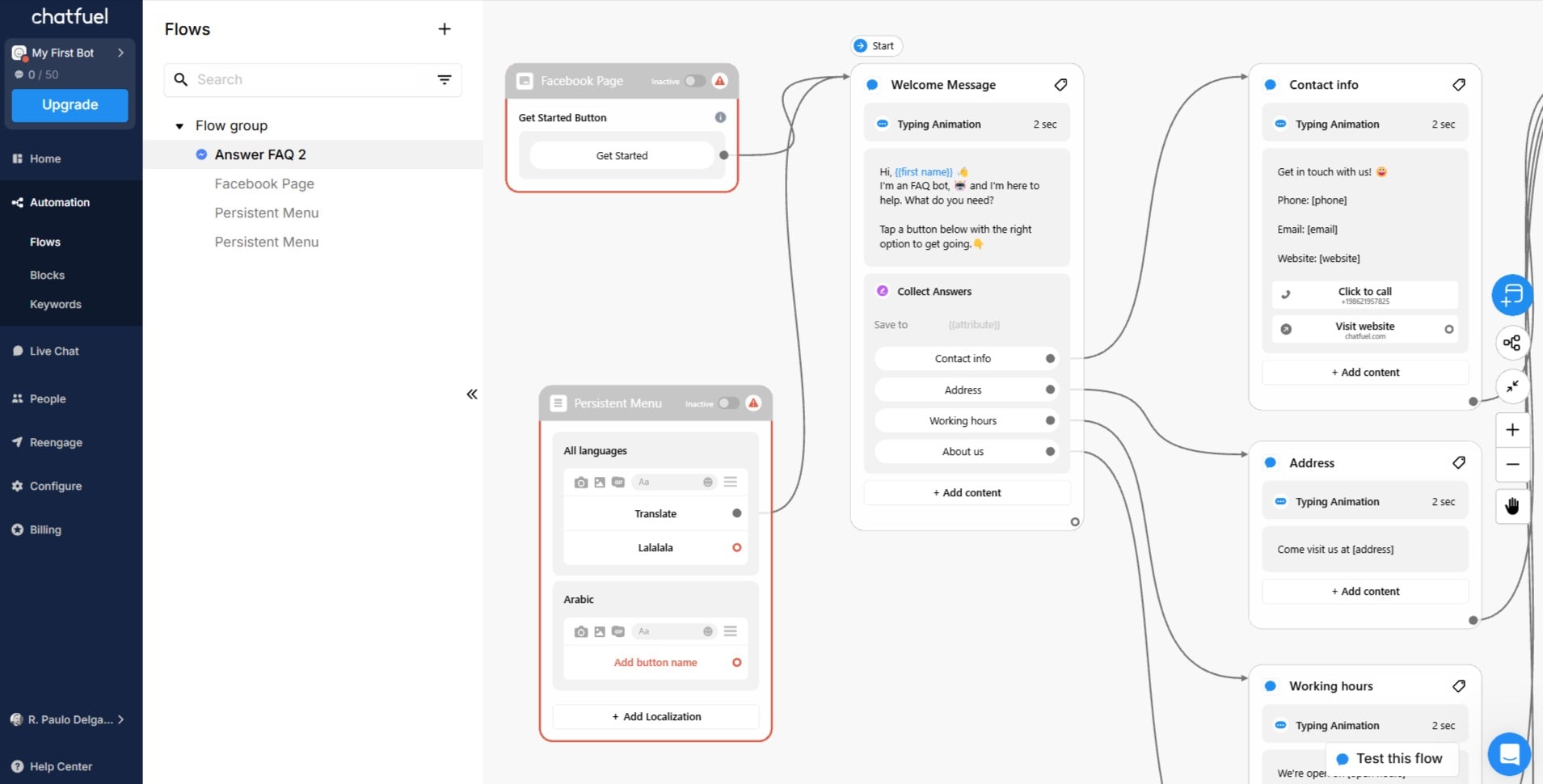
Chatfuel
AI-powered chatbots
Even the original ELIZA “chatterbot” used a primitive form of natural language processing (NLP) to try and extract the user’s meaning. NLP has progressed immensely since then. However, the recent advancements in AI have moved chatbots from NLP to NLU—natural language understanding.
Machines don’t “understand” things the way humans do, but modern AI can derive so much context from user input that it feels like the chatbot does understand the human’s query. Modern AI chatbots can therefore hold much more useful conversations because of their ability to determine the correct output from a user’s input.
Most people are familiar with generative AI, the subset of AI that generates text and images. Most of the AI chatbots springing up these days use generative AI as their base technology. However, it’s possible to use other forms of AI and machine learning to improve the functionality of these chatbots.
Done properly, AI-powered customer service chatbots can significantly reduce your company’s workload. In Spain and Italy, more than 80% of consumers chose to engage with a generative AI customer chatbot in 2024.
If you need help creating an AI chatbot for your business, reach out to one of Fiverr’s AI chatbot development experts.
Find an AI expert on Fiverr
Conversational chatbots
Using AI, it’s possible to create chatbots that use human language convincingly when responding to user queries. These chatbots are a subset of AI chatbots and are widely used to improve the customer experience and reduce wait times for customer service requests.
Unlike rules-based chatbots, conversational AI chatbots can make decisions based on context, making them flexible.
Some risks exist when using conversational AI chatbots because they tend to hallucinate—a technical word that means “answering with outputs which aren’t related to the inputs.” You can implement safeguards to minimize hallucination and to ensure your conversational chatbot answers mostly from your internal knowledge base. You can reach out to one of Fiverr’s many experts through AI model fine tuning services to get help to achieve this.
Messenger bots
Messenger bots are chatbots that operate specifically inside messaging apps such as Telegram, WhatsApp, or Facebook Messenger. They can be rules-based or AI-based. These chatbots can offer customer assistance or even integrate with an ecommerce platform to sell products.
Keyword-based chatbots
Keyword-based chatbots take actions based on keyword pattern recognitions. You must map keywords and phrases to specific responses.
Virtual agents
These chatbots pair AI technology with RPA (robotic process automation) to perform actions based on the chatbot’s output. The word “robotic” in this sense refers to anything automated, including software automation, not necessarily to robots. We talk more about virtual agents in the next section.
Find the best virtual assistant for your needs
How AI has changed chatbots
Before AI, it was impossible to create autonomous chatbots. You had to program every response and action the chatbot took. Setting up a chatbot in this fashion results in complex rules that can’t scale. These chatbots are also unable to interact convincingly using human-sounding language.
A subset of AI chatbots is the virtual assistant, also known as a digital assistant, predictive chatbot, or virtual agent. These are chat-enabled software programs that can perform actions based on your verbal or written input. They’re more advanced than chatbots because they can perform actions in addition to providing textual capabilities.
Two well-known examples of virtual assistants are Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri. Each uses NLP to understand user queries and then perform the relevant action.
The emergence of generative AI makes it easier for people to create a generative AI chatbot and virtual agent. Instead of spending days formulating rules based on “if this happens, then do that,” you can simply train your chatbot on your company’s data and then install it on your website.
You might need some help getting it installed or training it correctly, but it’s still much easier than it used to be. And you can get help from Fiverr’s AI website and software services to set it up.
How chatbots work
At their core, all chatbots operate this way:
Receive input from a user
Process the input based on underlying data and/or rules
Output an answer
(For digital assistants and virtual agents) Execute an action
Receiving input from a user
Receiving input is done typically in the same manner for all types of chatbots. The user will either enter a text query into an input field or send a voice message. Any voice messages are converted into text before the chatbot processes them, which requires voice recognition software.
It’s also possible to provide input to a chatbot automatically. For example, you could create a chatbot that ingests incoming emails and then provides assistance to users when composing a response.
Process the input
This is where chatbots differ significantly. Rules-based chatbots will process the input using the rules you’ve given them, and keyword-based chatbots will process it against a list of keywords. In both cases, an underlying data store must exist to store those rules and keywords.
For non-AI chatbots, the result of this process is deterministic, which means that the same input will always result in the same output.
Generative AI chatbots process input differently. Technically speaking, the large language models (LLMs) that underlie these chatbots are also a “data store,” but they don’t store the data itself. They store mathematical relationships and weights that map inputs to outputs based on how the model was trained. The model then uses these weights and relationships to understand context and provide contextually correct answers.
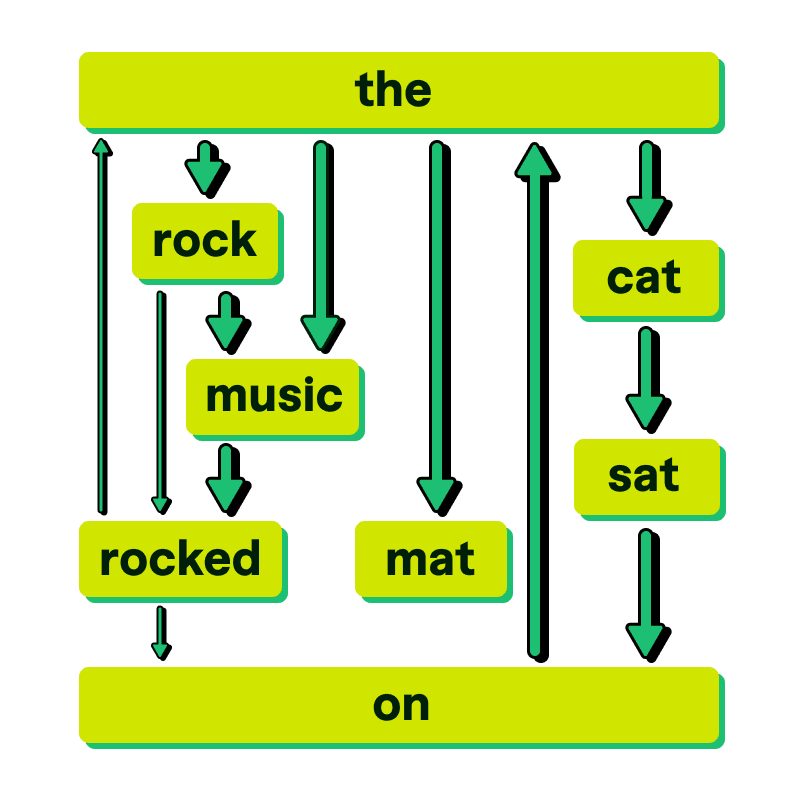
LLMs use weights between parameters to determine which fit best with others
For example, in the oversimplified image above, the thickness of the arrows represents the weighted connections between words in the LLM. Weights are adjusted according to which words fit best with which other words. Part of training an LLM is determining those weights.
Don’t worry if that sounds super technical. The important thing to know is that these mathematical relationships allow the AI model to determine connections that don’t necessarily exist in the underlying data.
The answers from an AI chatbot are non-deterministic, meaning you won’t always get the same answer for the same input. This ability to find different connections between data is what makes them so useful. However, it’s also what causes them to “hallucinate.”
The tendency of AI models to hallucinate is what has made regulated sectors slower to adopt them. Such sectors include healthcare, finance, and legal.
Even if you’re not in a regulated sector, it’s important to add a message in your AI chatbot clearly stating that the chatbot can make errors.
Output an answer
Once the chatbot has the answer, it outputs that answer as text or audio. All chatbots handle this similarly.
Execute an action (digital assistants and virtual agents only)
Digital assistants like Siri and Alexa can perform actions based on your input, but did you know it’s also possible to create your own virtual agent?
Unlike digital assistants, generative AI chatbots, such as those powered by ChatGPT, can only output text—they can’t perform actions directly. To enable actions, you’ll need to map the AI chatbot’s responses to a separate programmatic process.
For example, you can train the AI to output specific words when it determines an action is needed. You can then run the chatbot’s output through a keyword filter to trigger additional programming actions. A Fiverr chatbot development expert can help you do this.
Chatbot use cases
The rule of thumb is: If you can communicate it using words, you can create a chatbot for it.
Here are some examples of Chatbot use cases:
Ecommerce: Chatbots can handle customer service requests or help users pick their next product.
Healthcare: Chatbots can help patients book appointments and gather sufficient information about the patient’s condition to forward to a healthcare specialist.
Translation: You could program a chatbot to offer assistance in a user’s own language.
Marketing: You can run social media campaigns that ask users to comment on a post in exchange for a special offer or a freebie. A chatbot can then pick up the conversation and get the user signed up for a newsletter or upsell them onto a higher-valued product.
HR: Internal chatbots can help users find information from the company’s knowledge base, reducing new employee onboarding times.
Benefits of chatbots
Chatbots minimize the need for human intervention, offering 24/7 customer assistance. They can also manage multiple conversations simultaneously, lightening your team’s workload.
AI chatbots can provide contextual answers and deduce solutions that aren’t necessarily contained in their underlying data. Their setup time is minimal compared to more traditional chatbots.
If you pair your chatbot with RPA, you can create sophisticated virtual agents that perform actions based on user queries.
Hire AI chatbot developers from Fiverr
It’s never been easier and more affordable to create AI chatbots and virtual agents. APIs exist that let you use sophisticated AI models inside your chatbot. Whether you’re creating a mobile app or a web app, all you have to do is create the interface and then program the backend exchange of inputs and outputs with the API provider.
Find an AI expert on Fiverr
The pricing of these APIs is negligible compared to what it costs to create and run such high-performing models on your own servers.
Two commonly used APIs are OpenAI’s ChatGPT API, and IBM Watson, an AI natural language processing solution from IBM that’s been publicly available since 2013. If you need help with any of these API integrations, you can find plenty of API integration services experts on Fiverr
You can also get help from Fiverr app design services to help you design your chatbot’s frontend, or from Shopify development services to help you integrate a Shopify chatbot.
No matter what help you need, Fiverr has the talent to help you achieve it. Sign up for an account on Fiverr today and start finding the talent you need to move your business to the next level.
What is a chatbot FAQs
1. What is a chatbot used for?
Chatbots are software programs that provide real-time answers to user queries across different communication channels, such as on websites, mobile apps, or messaging apps. AI chatbots can use deep learning to improve the accuracy of their answers over time, while more traditional chatbots rely on rules and keyword detection to answer queries. Quality assurance plays a vital role in chatbot development by testing and refining the chatbot to deliver accurate, consistent, and user-friendly responses. Regular updates and evaluations help improve performance and the overall user experience.
2. Is Siri considered a chatbot?
Siri is a virtual assistant that uses chatbot technology, but it augments that technology by adding programmatic functionality based on your query.
3. Is Alexa a chatbot?
Alexa is a virtual assistant, also known as a digital assistant or predictive chatbot. These types of chatbots offer additional functionality than the typical chatbot and can execute programs and perform actions based on user queries.
4. What is an example of a chatbot?
Amazon Rufus is an example of a highly sophisticated AI chatbot that leverages machine learning, deep learning, and AI to optimize the customer journey.