How To Detect AI Writing: A Detailed Guide
This article details how to detect AI writing by combining manual checks with AI detection tools. You'll learn key indicators and practical techniques for recognizing patterns and inconsistencies
 November 14, 2024
November 14, 2024 9 minute reading
9 minute reading
The rise of generative AI, particularly tools like ChatGPT, has transformed the landscape of written content forever.
While many celebrate these breakthroughs in natural language processing and AI content editing, others harbor growing concerns about the future of authentic human expression.
As AI-generated text becomes increasingly prevalent, one question emerges: how can we distinguish between human and machine-written content?
This guide details how to detect AI writing. It covers the common indicators of AI-generated content and you can detect it accurately.
Find a AI Content Editor for Hire
An overview of generative AI
Generative AI extends far beyond ChatGPT. Leading tech companies have launched their own powerful tools: Google's Gemini, OpenAI's DALL-E for image creation, and Microsoft's Copilot integrated across Office products.
Content creation tools like Jasper AI and QuillBot can generate extensive written content in seconds, demonstrating the technology's rapid evolution and widespread adoption.
Let's look at some figures:
Generative AI's global market size will reach $36.06 billion in 2024.
A large portion of generative AI users are Millennials and Gen Z, and most of them hold jobs. Around 70% of Gen Z use the technology, and 52% trust it to help them make smart choices.
ChatGPT’s site currently has over 130 million visits monthly.
Three out of five workers use or plan to use generative AI.
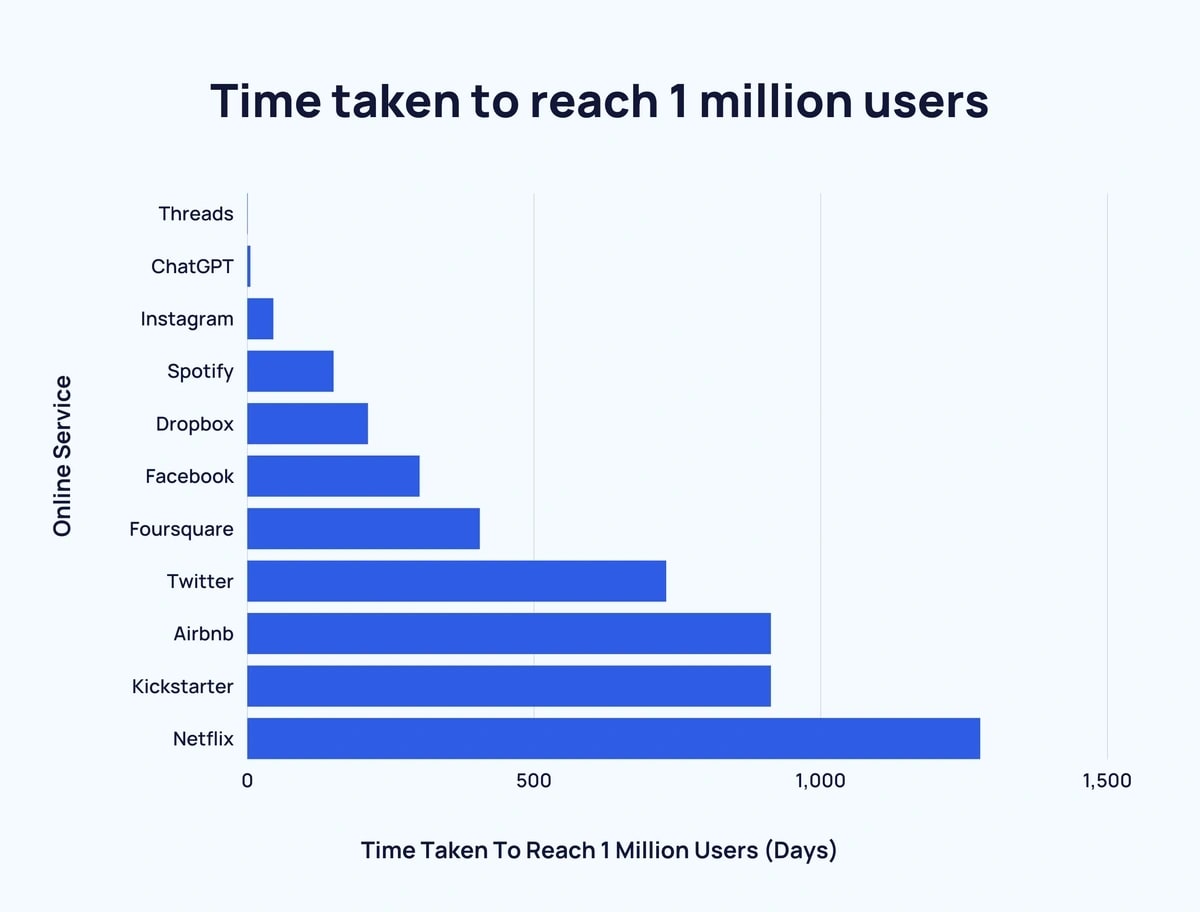
OpenAI reported that ChatGPT gained one million users just five days after its 2022 launch. To put it in perspective, Instagram took almost three months to reach a million downloads. It took Netflix over three years to hit the one million user mark.
Exploding Topics
To borrow a slang term from the new generation, the world of writing and copywriting is "shook."
The concern with the proper use of these language models isn't unfounded. It revolves around the potential issues surrounding AI, such as ethical implications and the spread of misinformation.
There are many ways to misuse AI. It can spread false information, especially on vital topics like health and politics, which can be hazardous. It can manipulate public opinion. AI is making it easy to create propaganda outlets. Their content can be hard to tell apart from real news. And at its core, AI can perpetuate laziness and deceit.
But all is not lost. There are ways to protect content against such potential misuse. Editors, educators, and marketers can vet content manually or use AI detector tools.
What’s considered AI writing?
A human wrote this article, not an AI tool. That said, AI has written thousands of articles since 1967, when Alison Knowles used FORTRAN, a programming language, to write poems.
In 2020, the Guardian published an editorial titled "A robot wrote this entire article. Are you scared yet, human?" The piece was entirely generated by GPT-3, OpenAI's language model, which was tasked with convincing readers that robots come in peace.
This watershed moment marked one of the first times a major publication had featured an AI-written article, sparking intense debate about the future of journalism and raising questions about the role of human writers in an increasingly automated world.
Four years later, AI writing produced scores of:
Marketing ads
Product descriptions
Social media captions
Resumes
Q&As
Academic papers
So, what is AI writing? Should humans be scared of it?
AI writing includes any text fully generated or significantly shaped by artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT, Jasper AI, or Google Gemini. It differs from content that simply uses AI tools for basic grammar checking or minor edits, as AI writing involves the technology generating or substantially rewriting the core content.
AI jargon is confusing, so let's try to simplify how this works:
AI uses natural language processing (NLP) and natural language generation (NLG) to produce human-like written work.
LLMs use neural networks. These are computer systems that mimic the human brain's structure.
LLMs are trained on huge datasets that include texts and images to recognize patterns.
These algorithms analyze millions of web pages. They study patterns of human-written content, including sentence structure and tone.
Edureka
Perhaps you've heard of GPT-3.5 or GPT-4? These are popular examples of LLMs developed by OpenAI. For all intents and purposes, AI writing makes users' lives easier. Just write a prompt for what you want; AI tools will generate content in seconds.
This makes AI programs and apps create content that sounds human. They've processed and learned billions of sentences. So they "know" the likely words, their order, and the context.
For businesses and brands, AI is used in two ways:
Building their own language models
Many businesses, especially in tech and marketing, use company data to develop their own language models. These language models have specific functions, features, and goals depending on business operations. Once trained, these models can generate various content and streamline operations. For example, visitors can get information directly from the company’s chatbot.
Using publicly available language models
Most businesses implement AI using publicly available models like GPT-4. These public language models can perform broader tasks and access any public data from the internet. To be on-brand, companies fine-tune them for specific tasks so they can generate brand-specific news articles, SEO content, social media posts, and customer service responses.
It's not only companies that use these public language models. Individuals like freelancers, bloggers, content creators, and students use them to create content. Projects that used to be researched and written for days can now be delivered in minutes.
But with all the wonderful perks AI writing can provide, it poses major challenges. It's not human, so it lacks the human touch. It can't add emotional nuance to text. It can't innately provide personal anecdotes or experiences. Also, it learns only from other content, so it's prone to plagiarism and monotony.
AI tools can also hallucinate in their outputs. They essentially guess the best response to the prompt. Their success rate is high due to their vast training data. But they can and do make mistakes.
Why? Because even the most sophisticated AI writing tool needs a human to make it work. These intelligent machines (still) can't do the tasks on their own. They need someone to enter prompts or set guidelines. These include the topic, point of view, goal, tone, length, emotion, and complexity. When the human hits “enter,” that's only the time AI gets to work. And even then, fact-checking and AI content editing by a human is a must.
Why is detecting AI writing important?
TIME recently posted an article by Victoria Livingstone. After almost 20 years of teaching, she won't return to the classroom. She quit, in large part, because of LLMs like ChatGPT. She noted she spent more time grading AI-generated writing and giving feedback to AI tools than her students.
This is how AI has changed the course of copywriting, academic writing, creative writing, and more.
Ethical and integrity concerns
AI often finds itself at the center of ethical and integrity controversies. AI writing tools even sparked a writers' strike in 2023, causing major disruptions in film and TV. The question is, even if ChatGPT and similar tools can write a whole movie script, should they?
Using AI content marketing tools raises questions about originality and authorship. If an article is "written" largely by an AI tool, is it right, ethical, or legal to credit a human author? It blurs the line between human and machine work, undermining original thought and expression. These ethical lines can even cause legal issues.
Also, machine work can worsen current biases and inequalities. AI is only as great or harmful as the data it learns from. An AI tool trained on biased data will produce biased output. These biases may perpetuate discrimination against marginalized groups.
Impact on education
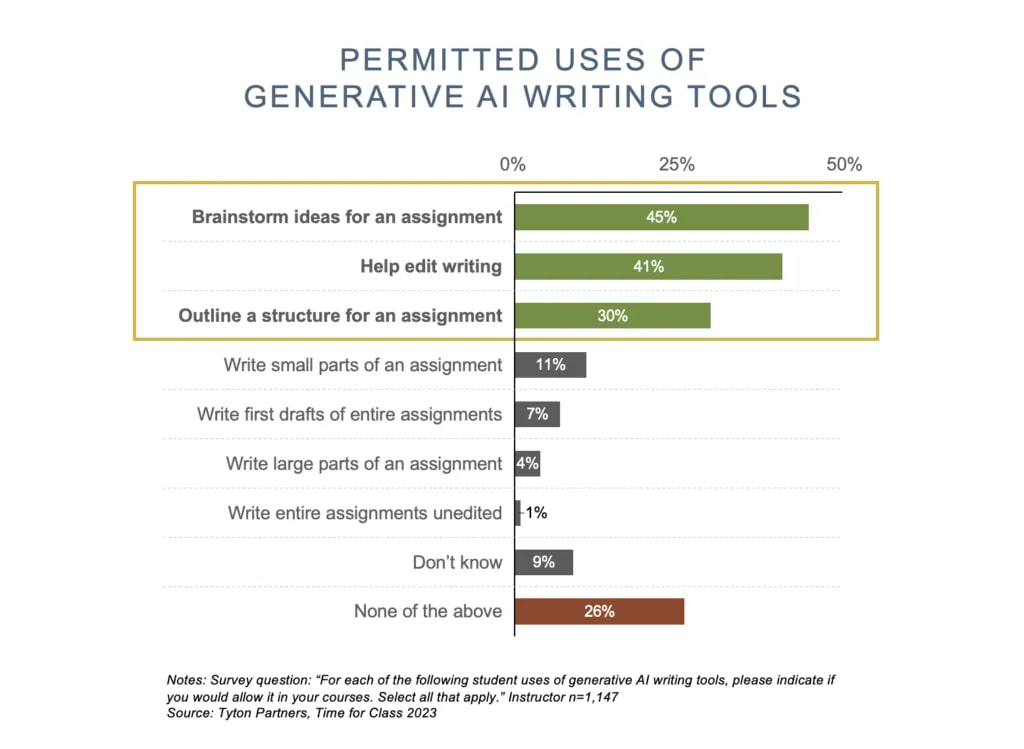
Education is one of the many major industries affected by AI and one of the first to realize that generative AI is here to stay. A Turnitin study found that three times more students than faculty used generative AI tools. When ChatGPT was launched, many schools tried to ban its use. In the same study, 46% of students would use generative AI tools despite bans by their teachers or schools.
Students who use AI to write their assignments aren't cheating or plagiarizing. Technically. After all, no original work is being copied. However, the paper isn't also the student's original work. To that end, using AI to write and submit a paper as one's work is academic misconduct.
And it's not just daily assignments that are in question here. AI writing can create academic papers, theses, essays, and even school applications. These days, most instructors encourage using AI to generate ideas but set limits when writing full text using AI.
Tyton Partners
Misinformation
Generative AI is the ultimate disinformation tool. It can quickly create vast amounts of fake content, expound on the problem of disinformation, imitate real people's voices, and create fake photos and videos with malicious intent.
Misinformation in marketing, journalism, and PR can harm brands at best and be life-threatening at worst. During polarizing times, like a national election, information is vital. But with advances in AI and technology, it's harder to tell real news sites from fake ones.
Virginia Tech noted that, since the rise of the internet, groups have been able to create websites with fake news. This propagation of disinformation pre-dates the AI revolution. Now that AI writing is in full swing, detecting fake news takes precious time. LLMs inadvertently enable bad actors to produce and spread what appears to be accurate information. All this presents danger in our society.
Credibility
Credibility is tied to misinformation. It's not unheard of for major companies and institutions to use AI to streamline their work and produce content quickly. Associated Press became the first newsroom to use an AI editor in 2014. However, over 1,100 unreliable AI-generated news sites operate today with little to zero human supervision.
The one thing about AI writing is that it warrants rigorous fact-checking. Regardless of the company size, every business that uses AI in content marketing must conduct comprehensive AI detection with all its articles. Without doing so, they risk damaging their credibility. It could also cause ethical and legal issues for companies.
What does Google say about AI content?
Google has long believed that AI can transform information delivery. Appropriate use of AI isn't against its rules. The key word is "appropriate." So don't use AI to create content that tricks search engines into ranking it higher. Doing so would break Google's spam policies.
Google Search Central
Here are some key points regarding Google's stance on AI content:
Google's ranking system prioritizes E-E-A-T: Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. This means Google values content quality over its creation.
Using automation, like AI, to create content that manipulates search rankings is a violation. To fight such content, Google uses spam-fighting tools like the SpamBrain system.
Google Search doesn't ban AI content because it also has value.
Poor-quality AI content taking over SERPs isn't a new issue for Google Search. The company has dealt with this issue from human and AI-written content for years. They have a system that evaluates the value of content and ranks them accordingly.
Google will handle AI-generated content that spreads misinformation like human-written content. Google's systems focus on showing high-quality search results from reputable sources. They avoid content that contradicts widely accepted facts.
Can AI tools really detect AI-generated content?
Find a random article online. Run it on three different AI detector tools, and you'll likely get three different results. Some flag false positives, confusing written content for AI content. Others flag an article based on trivial elements, like headings in question form. But beyond structures, most AI detectors fail to spot deepfakes and machine-generated text.
As tempting as it might be to rely on AI detector tools solely, you shouldn't. Like AI tools, they're trained to uncover patterns and structures. They use machine learning and natural language processing. Their training is also dependent on the developer's bias.
As such, they’re also susceptible to mistakes and inaccuracies. Even OpenAI's AI Text Classifier was discontinued due to its low-rate accuracy.
Here are the limitations of AI detection tools:
Since AI writing tools are trained to mimic how humans speak, separating AI content from human-written work is challenging. Now, the last thing you want to do is to accuse a writer of using AI if they genuinely haven't. You wouldn't want to be the topic of a subreddit forum.
AI detector tools have advanced but lag behind AI content generators. As a result, they always play catch-up, making their results unreliable.
If the AI detector tool is trained on older models, it will be inaccurate when it comes to detecting content from the latest AI tool. Some AI detector tools prefer huge chunks of paragraphs and flag outputs with bullet points. Others prefer listicles to long-form prose text.
A Cornell University study found that some AI detectors misclassify non-native English writing as AI-generated. This is yet another example of AI bias.
These limits don't mean to undermine AI detectors. They can genuinely be useful—maybe not in foolproof detection but in helping point out signs of possible AI-generated content. Ultimately, manual checking is needed. It plays a huge role in determining whether a machine or a human writes an article.
How to detect AI writing
AI detector tools have value, especially paid ones, since they have more features. However, to give you the best chance of detecting AI writing, combining it with manual checks is a must. You can do the manual checks yourself or hire a professional.
Fiverr, for instance, has a host of experts who can differentiate AI content writing from human writing. If you're doing the spot-checking, pay attention to the following:
1. Repetitive phrases and ideas
Using repetition isn’t inherently bad. It's handy to repeat ideas to help readers remember your message. But repeating phrases to pad the word count is not. Repeated words, phrases, and sentences are a clear sign of AI-generated content.
AI is trained to recognize patterns and replicate them. Unsurprisingly, you'll see the same sentence reconstructed repeatedly in different paragraphs within the article. Even OpenAI stresses this limitation. The model is too verbose and overuses some terms.
Aside from repeated words, look for keyword stuffing. Since prompts are used to generate an AI output, users often include keywords in the prompt. This usually causes excessive and incorrect keyword use.
Check this AI-generated answer from ChatGPT. Note the highlighted words.

ChatGPT
Although it answers the question "What is cultural appropriation?", ChatGPT's response repeats itself. "Respecting," "borrowed," and "appreciation" convey similar ideas. They all acknowledge and value cultural elements, which are emphasized several times. "Borrowed" also means using cultural elements without respect, echoing the underlying point.
A human writer can relay the same idea more succinctly because they recognize redundancy. When writing the article yourself, you can read it aloud and spot repeated words and thoughts. As such, you can easily remove or revise duplicate parts of the article.
2. Common phrases and idioms
Idioms often present a stumbling block in translation. However, LLMs trained on vast text data can reasonably use idioms. At this point, AI language models use idioms more frequently than human writers. So it's important to check for sentence structure variations.
Do the used idioms flow naturally within the sentence? Do they add value to the sentence? Sentences with idioms must be grammatically correct but don't feel forced.
If you've used AI generators for a while, you’ll notice that ChatGPT and similar tools have favorites. They put the same idioms and phrases on rotation. AI Phrase Finder noted the top 10 idioms ChatGPT uses. These include:
Cut corners
Think outside the box
Break the ice
It's not rocket science
Snowball effect
Perfect storm
Back to the drawing board
Raise the bar
Get out of hand
Go the extra mile
Meanwhile, the most common phrases generated by ChatGPT are:
It's important to note that
In this article
Master the art of
In summary
A testament to
In the dynamic world of
A tapestry of
Delve into
Embark on a journey
A treasure trove of
In this digital world
When it comes to
In the annals of
So go ahead
In the realm of
Sure enough, when you run the most common phrases ChatGPT uses in ZeroGPT, an AI detector, it flags several phrases:

ZeroGPT
Sure, human writers also use idioms in articles, but not excessively; at times, not even sparingly. This is particularly true of writing that tackles serious topics or needs a serious tone, like a legal document.
3. AI typical words
If one word is the surest sign of AI writing, it's "delve." ChatGPT even joked about it:

ChatGPT's X
So does this mean any article with the word "delve" in it is AI-generated? Absolutely not. Human writers have used the word for years. However, it's better to be cautious of words that sound vague and mechanical. If you use them far too many times in a piece of writing, your piece may be flagged as AI-generated.
Here's a Reddit forum of overused ChatGPT terms that you can look into. Medium also listed the common words used by AI. Here's an overview:
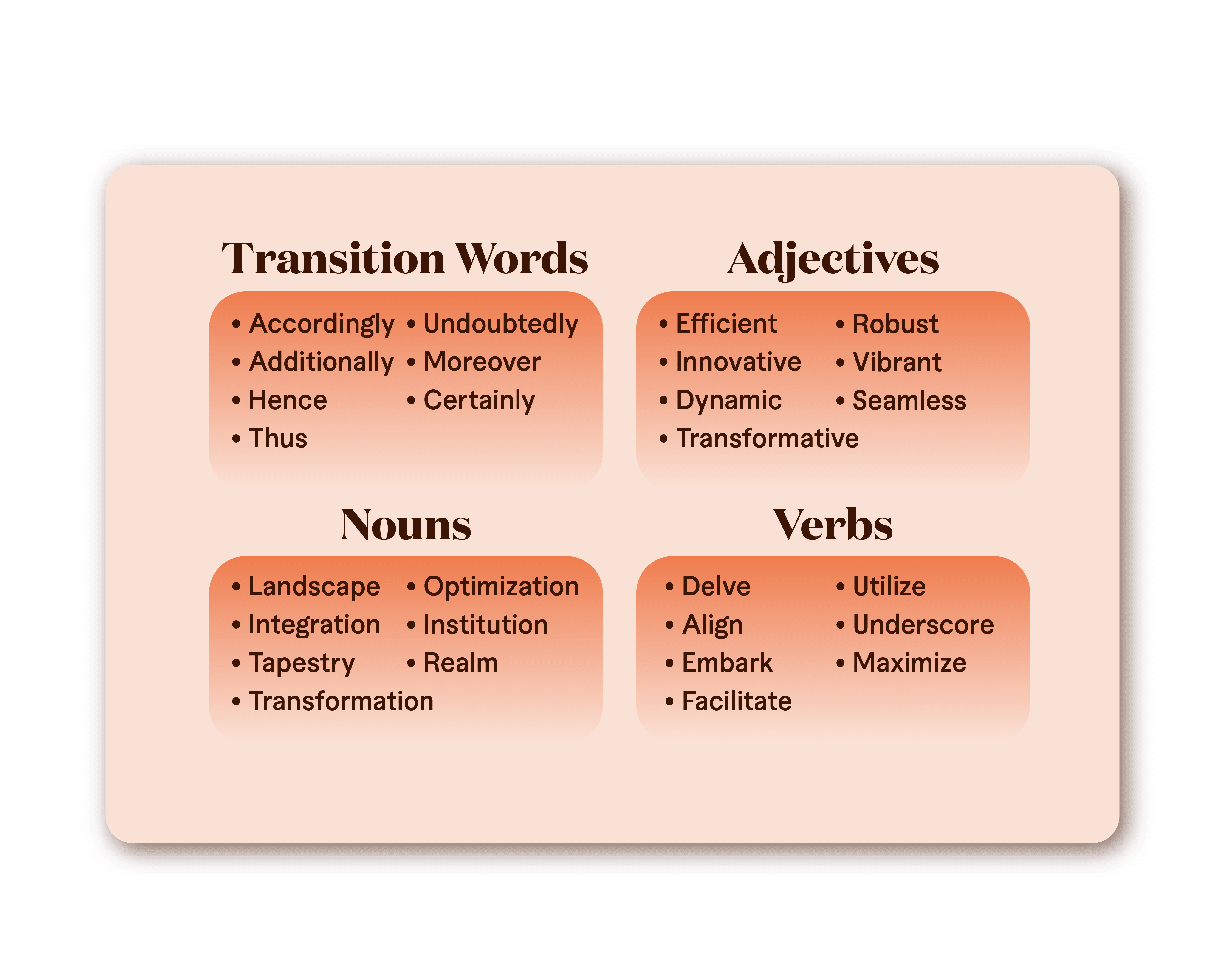
This is where you need to evaluate the piece fairly. Some of the listed words appear in AI content writing and human-written articles. For instance, "optimization" and "seamless" are often used in marketing, so just be mindful of not overusing these terms. Also, consider actual conversations. Have you heard of "realm" used in casual chats outside gaming?
To check whether the writer chooses to use the word or a machine generates it, we suggest you do AI content editing. Hire someone to spot-check your piece and rephrase sentences that may trigger false positives.
4. False claims
At first glance, an AI-generated article looks and sounds professional and well-written. Suppose the user learns to revise or remove repetitive phrases and use synonyms for overused words. In that case, the article can easily fool AI detectors. So the next thing on your list must be manually fact-checking the article.
Most AI language models lack real-time access to data, so they may give outdated information. Based on their training, their responses can also be misleading. This can be dangerous for certain subjects like healthcare, which is why most have disclaimers on the health information they generate. These models can also have artificial hallucinations, as mentioned above.
Fact-checking can be time-consuming but is pretty straightforward. If you're checking an article full of stats and figures, a simple Google search can give you an answer. Look into reputable websites as sources.
Also, when editing an article with product descriptions, check all information with the brand to avoid misrepresenting it.
5. Boring tone of voice
There’s no substitute for human context. Even the most advanced AI can't write with human emotions. They can mimic joy or sadness by using phrases related to both feelings but can't put the right tone to it. Even formal documents written by a person come with a tone.
Monotone is one of the most glaring signs of AI-generated content. Machines don't use slang or informal language unless prompted. They don't have humor. They don't joke. All in all, they lack personality and humanity.
Look at ChatGPT's response to a prompt to describe the movie "A Walk to Remember."

ChatGPT
A human writer wouldn't present the description as stiffly. They wouldn’t list the characters' names in bullets or use over-the-top words to describe the plot. A human writer will add personal anecdotes and emotional nuances to connect with the readers.
6. Generic explanations
After reading the whole article, answer this: did you learn anything specific?
If there's a conspicuous shortage of specifics in the article, it's usually a sign of AI-generated content. AI language models use universally known details instead of presenting specifics about the subject. If the piece only provides vague descriptions, then be wary.
For instance, the machine would reply, "The cities…", but a person would actually list the cities. They can do so because they've researched. AI would list possible recommendations. A person would give actionable advice, especially if they have relevant experience.
This generic explanation results from all the red flags we've discussed: repetitive ideas, word padding, outdated data, and a monotonous style. AI can make an article look complex, but if you look closely, it's just a bunch of long, fluffy sentences.
AI detection tools
Again, we emphasize that AI detector tools are valuable. After all, developers created them with a clear goal: to spot AI content. However, not all are equally designed, so use your judgment to find the best detector tool. Here are three that are making waves in the market today:
Originality.ai: This advanced three-in-one tool can check content for AI writing, plagiarism, and facts. It focuses on textual patterns and linguistic nuances for AI checking. One of its top features is multilingual capabilities, enabling it to recognize cultural nuances. Pricing starts at $19.95 a month.
Turnitin: Turnitin is more than just a popular plagiarism checker. Today, schools and educators use the tool to detect AI writing. Turnitin AI detector shows text manipulations and gives a detailed similarity report, which helps explain why the AI flagged the content. It also has a dashboard for educators' insights.
Writer: This tool's AI detection is part of a full-stack generative AI suite to improve work. Its AI checker tool evaluates and then rates the article to see if it's human-generated. The best part is that you can check up to 5,000 words for free.
Hire writers and editors on Fiverr today
If written content is a large part of your work, you must always engage readers with fresh content. AI isn't an enemy in this regard. Using it wisely can help you brainstorm ideas on what topics and trends you can explore. What you don't want to do is to heavily rely on it when writing your content. People will connect with content written by people. There's no circumventing that reality.
If you feel unqualified to create written content, we're here to help you. Fiverr has exceptional writing services that cover anything from blogging to ghostwriting. We also have AI consulting if you want to learn how to leverage AI in your business. Lastly, we have writers that can humanize your AI content. Explore our services today to see which one will benefit you the most.
Detecting AI writing FAQ
Is there a way to detect AI writing?
Yes, there is. You can use AI detector tools or hire editors who manually check for AI writing.
How do teachers detect AI writing?
Teachers can use AI writing checkers to detect whether an article is AI-generated. They can also check for repetitive words, ideas, vague explanations, outdated info, and a monotonous style.
How do you check if AI wrote a document?
Combining manual checking and AI detection tools is a good way to see if a document is AI-generated.
How do you make your AI writing undetectable?
A good way to make your AI writing undetectable is to write it yourself (or hire a Fiverr writer).
How to make ChatGPT answer undetectable?
While challenging, you can revise a ChatGPT response to make it undetectable. Add some personality and personal anecdotes. Ensure all info is detailed and fact-checked. Use a variety of sentence structures.