What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and How It’s Changing SEO
Discover what GEO is and how to optimize for AI-generated search answers.
 May 25, 2025
May 25, 2025 8 minute reading
8 minute reading
Unless you’ve been on hiatus from LinkedIn for the past year, you’ll know GEO is the new hot thing in digital marketing. It involves optimizing your web content for AI search engines like ChatGPT and Google AI Overviews.
But is it any different than SEO?
If you look under the hood, not really. The same practices apply to get more mentions in LLMs (GEO) as ranking higher in SERPs (SEO), just in a slightly different format.
Ahead, you’ll learn how to incorporate GEO into your SEO strategy and improve mentions in LLM.
What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization is the process that maximizes how often and prominently AI-driven search engines like ChatGPT, Google’s AI Overviews, and Gemini cite your pages.
Unlike traditional search engines, GEO optimizes for:
The datasets that large language models (LLMs) train on.
The citations and snippets answer the engine's surface.
Signals like schema markup, clean site architecture, and high-quality content that LLMs can parse easily.
In a 2024 research paper, the authors found that simple page edits (inserting statistics, quotations, or explicit citations) raised citation share by up to 40% across diverse topics.
Traditional search engine optimization tricks actually reduced LLM visibility, while tactics like “Quotation Addition” and “Statistics Addition” topped the leaderboard in both objective and subjective impression metrics. Great GEO starts by matching user intent rather than keyword research.
GEO matters for many reasons:
Clicks are evaporating. Ahrefs’ study of 300k keywords shows that when an AI Overview appears, the position-one page loses 34.5% of its clicks.
Answer boxes are multiplying fast. AI Overviews have grown by +116% since March 2025 and now show on roughly 12% of US Google searches.
Search was already going “zero-click.” Even before AIO, SparkToro found that ~60 % of US user queries end without any outbound clicks.
More folks are using generative engines for search. In 2024, around 15 million US adults used genAI as their primary tool for online search. By 2028, that number is expected to reach over 36 million, as per Statista.
As content volume explodes, visibility inside LLM outputs will become the new scarcity. GEO is how marketers compete for it.
GEO vs SEO: Key differences and overlaps
If you’re here, you already know what SEO is. And in fact, GEO and SEO share plenty of similarities. Both exist to:
Win attention the moment a question is asked, whether in a search engine results page or a ChatGPT window.
Channel that attention into traffic and revenue.
Measure success with downstream KPIs (sessions, sign-ups, and sales).
However, there are plenty of differences between the two.
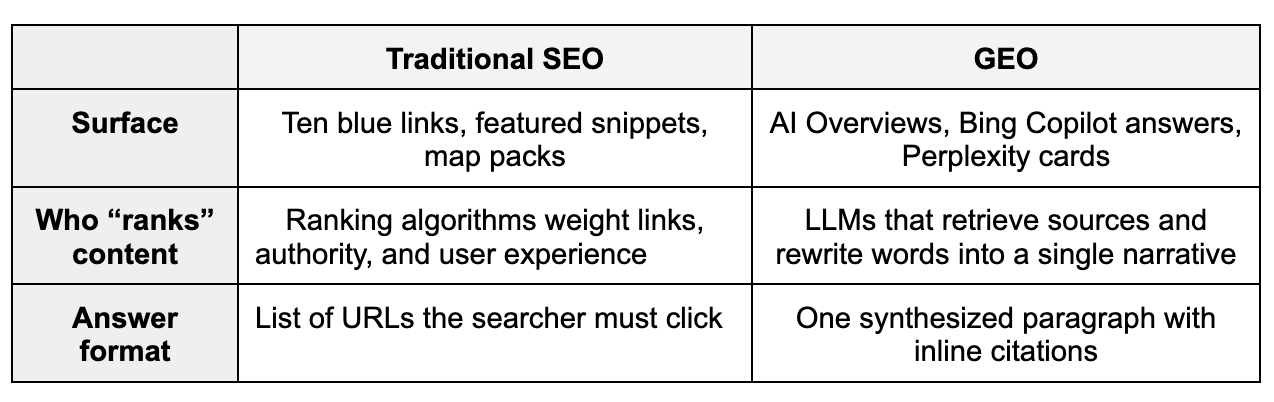
Another major difference is the black-box nature of GEO. Marketers have long optimized for Google’s known (and partially documented) ranking factors. Generative AI models are less transparent in how they choose which sources to trust or cite.
The tactics that work are also different. The GEO study shows that keyword stuffing, once a crude but workable SEO shortcut, actually depresses LLM visibility by roughly ten percent compared with leaving the page alone.
💡 SEO still feeds the organic search beast. Generative engines start with a search retrieval step, so good technical SEO and website content keep you in the candidate pool.
GEO is the second layer and makes sure LLMs can parse, quote, and credit your expertise even when users never click a blue link.
How GEO fits into your marketing strategy
Brand awareness, conversions, and trust
Generative engines rope your sentences in the answer box. When that paragraph is the interface, a citation is the billboard. That real estate means more branded impressions and, because the engine links each sentence to its origin, built-in credibility.
Well-linked domains have always dominated SEO, but GEO gives challenger brands a chance to leapfrog. Pages that sat fourth or fifth in Google’s organic results gained between 97% and 115% more citations after GEO tuning.
Think about what that means. Whether you run small business SEO campaigns or compete at an enterprise SEO scale, GEO lets you punch above your weight and steal conversions from competitors.
And if you’re wondering what this SEO-tactic costs, project-based GEO sprints often beat long-term retainers on ROI.
Tactical shifts marketers need to make
To turn GEO from idea to impact, you’ll need to re-engineer the copy itself. Structure every stat, quote, and citation so that large language models can parse, trust, and showcase it. Do the following:
Format for machine parsing. Add explicit numbers, authoritative sources, and quotations. The GEO study found that those micro-edits are the single biggest visibility boosters and work across domains.
Include citations as a feature, not an afterthought. “Cite Sources” alone can push a line of copy 132 percent higher inside Perplexity’s answer pane. Explicit citations bolster E-E-A-T and help LLMs choose you.
Have prompt-sourcing awareness. Engines usually feed the top five Google results into GPT–type prompts before writing the answer. So, technical SEO still gets you into the room, but GEO makes you speak up once you’re there.
Stack methods. Pairing Fluency Optimisation with Statistics Addition outperforms any single tactic by another 5-6 percent, as per the study.
Find a Generative Engine Optimization specialist for hire
GEO-first content briefs
GEO works best when it sits on top of a solid content strategy that already targets your audience’s pain points.
This will influence your content briefs, too. A GEO-first brief clarifies many of the tactics mentioned above. Here is an example:

Examples of brands winning LLM visibility
The GEO study references a few observed case studies:
Swiss-chocolate bloggers added a single citation from an international consumption survey and saw a 132 percent lift inside the answer card.
Robotics-consultancy site inserted a fresh industry statistic (“70% rise in workplace robots”) and gained 65 percent more answer share without rewriting the page.
Sports-news upstarts embedded four division-title facts for the Jacksonville Jaguars and nearly doubled their presence versus ESPN in LLM summaries.
How to optimize content for generative engines
1. Structure answers so AI can lift them verbatim
Write copy that slots cleanly into AI-generated responses. Put a numeric data point or expert quote in the first 250-300 words.
Position-Adjusted Word Count scores words higher the earlier they appear, and simple Quotation Addition / Statistics Addition lifts visibility 22-37 percent on live Perplexity tests, as per the GEO study.
Use inline bracket citations right after a sentence. LLMs can better read this format and boost “Cite Sources” pages by up to 132%.
Also, chunk with scannable headings and lists. Fluency Optimization—shorter sentences and clear structure—adds another 15-30 percent visibility on its own and pairs best with Statistics Addition.
2. Add machine-readable signals
“Machine-readable signals” means any piece of information added to a page for an AI algorithm to interpret.
For generative engines, those signals tell LLMs what to quote and whom to credit when it decides on answers.
Some ways to do this include:
FAQ schema. Add an FAQPage block beneath a section header. Each Q/A pair becomes a self-contained fact that the LLM can pull verbatim, increasing your chances of being cited.
Numeric facts with units. Instead of writing “AI Overviews show up more often now,” write “Google AI Overviews appear on 16 % of U.S. queries—up 116 % since March 2025.” The number + unit pattern is a high-signal datum that fits neatly into the engine’s structured response.
Citation-friendly formatting. Place the statistic or quotation in the first 300 words and attach a bracket citation. The GEO study shows these two micro-edits—Statistics Addition and Quotation Addition—can raise visibility by 30-40% with no other changes.
These signals matter because generative engines build an answer in stages. They fetch the top Google results, chunk the text, then run a summarizing model to blend the sentences together with inline citations.
If your page already:
Labels entities explicitly (via schema),
Presents facts in clean, atomic sentences, and
Uses the same citation syntax the engine expects,
Then the model can drop your words into its narrative as-is, skyrocketing your share of the answer box without needing extra backlinks or keyword tweaks.
3. Create trustworthy, well-cited, and linkable content
Before you publish that blog post, make sure it covers the following criteria:
Include third-party authority. A one-sentence quote from an identifiable expert or a government statistic beats a paragraph of adjectives, because LLMs favour verifiable atoms over prose.
Swap adjectives for numbers. Replacing “many” with “70%” (plus citation) is the single biggest lift measured across nine domains.
Show your homework. Outbound links to primary research won't leak clicks when the engine is already summarising; they simply raise trust signals the model can cite.
4. Build the right tool stack
Equip writers with AI tools that help them improve content visibility. Here are some of the top options.
Research and ideation
Start by seeding your brief with fresh, verifiable data and quotable experts. Ahrefs Content Explorer is still the fastest way to surface recently linked studies. Statista and Pew Research supply timestamped, quantitative nuggets that convert well into Statistics Addition edits.
If you need something industry-specific, plug target queries into Perplexity.ai and scan the inline citations it returns. Those sources are “LLM-ready,” so borrowing a stat from them increases the odds you’ll be cited too.
Draft optimization
Once you have the written draft, run it through an on-page optimizer like Clearscope. Create a custom brief template that encourages writers to place a numeric fact and an expert quotation in the first 300 words, each followed by inline brackets.
If you’re working in ChatGPT, use a prompt to get helpful stats or quotes. Here’s an example of an add-a-stat prompt:

LLM visibility rehearsal
Before you publish, “rehearse” the page inside an answer engine. Upload your draft as a source in Perplexity’s file mode or paste the URL into Bing Copilot, then ask a target query.
Watch which sentences get quoted: if your stat or quote doesn’t appear, tweak placement or clarity until it does.
5. Add llms.text
llms.txt is a proposed standard that sits beside robots.txt and sitemap.xml.
The idea is to drop a text-file at yourdomain.com/llms.txt that lists the URLs (API docs, product specs, policies, FAQs, etc.) you most want LLM crawlers to ingest.
It claims to give LLMs a clean content map so they don’t waste tokens guessing what matters. No model (like OpenAI, Anthropic, or Google) has publicly committed to obeying llms.txt.
Will it hurt? No. Could it future-proof your site if the spec catches on? Sure. That’s why it’s worth your while to publish a live llms.txt using a tool like Firecrawl or hiring a developer with AI coding skills.
Find an AI machine learning expert on Fiverr
How Fiverr freelancers can support GEO needs
GEO is a multi-disciplinary sport. You need research, copy, technical knowledge, and measurement.
Few in-house teams have specialists for every task, which is why a talent pool like Fiverr is handy. You can spin up niche support for bursts of GEO work without bloating payroll.
Some SEO services you can find on Fiverr include:
Data hunters and fact-checkers. Hire web researchers to trawl academic journals, government reports, and trade reports to surface numbers and quotes.
Writers and editors. Partner with SEO content writers and proofreaders to weave stats and quotes into articles and improve the quality of your final product. Or bring in technical writing services to translate jargon into LLM-friendly language.
Technical SEO experts. Get help creating structured data and validating the results through Google’s Rich Results Test.
Prompt engineers. Build reusable prompts that can produce authoritative content that's on brand.
Reporting automation. Experts can compile weekly snapshots of which URLs surface in Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, and Perplexity.
Tap a global bench of niche experts and AI services just long enough to ship each optimization sprint, then scale down. That agility lets you chase every new AI-answer surface without waiting for annual budget cycles or full-time hires.
GEO FAQs
What is generative engine optimization?
GEO is the practice of writing and formatting your web pages so AI tools like ChatGPT or Google’s AI Overviews can easily grab a line from your site and show it in their answers. It’s basically making your content easy for robots to quote, which many consider generative AI engines the future of search.
How is GEO different from SEO?
SEO tries to push your link to the top of a Google results page. GEO tries to get your exact words—like a stat or quote—from that page dropped right into the AI-generated answer box, so people see your brand even if they never click a link.
Can GEO replace SEO?
No. Good SEO still gets your page into Google’s top results, and AI systems often start by scanning those same pages. GEO is an extra layer you add so the AI actually uses your content once it finds you.
What tools help with GEO?
Research tools like Ahrefs or Statista find fresh numbers and expert quotes to include. Editors such as Clearscope or Surfer make sure those facts sit near the top of your draft, and free schema validators check that your markup is clean.
How do I get my content featured in ChatGPT or SGE?
Put one clear statistic or expert quote followed by a citation in the opening paragraph. Wrap key info in FAQs or How-To schema so the AI can read it.
Then run the draft through an AI answer engine. If your sentence shows up in the answer box, you’re set. If not, move it higher or make it clearer and test again.